2. FAQ - Server Issues¶
2.1. How to change correctly my CA (SSL/TLS) certificate¶
2.2. What procedure should I follow if my WAPT server is inoperative (fire, flood, physical destruction)?¶
Note
Assess the level of urgency:
Determine whether the situation requires immediate action. For example:
Case 1: If you need to install a new package or an urgent update, the urgency is critical and rapid action is required.
Case 2: If you don’t regularly use updates via WAPT, new packages, deployments or reporting, you may have a few days, or even a week, before taking action.
Note
If you have an external backup solution, you can follow this documentation to easily recreate the WAPT server.
This suggested solution only applies if you have an Active Directory and many agent machines that are members of your AD.
1- Create a new server:
The quickest solution is to recreate a server. You can follow the links below:
Check the server requirements.
Install the server according to the OS.
Launch the WAPT console and create an agent.
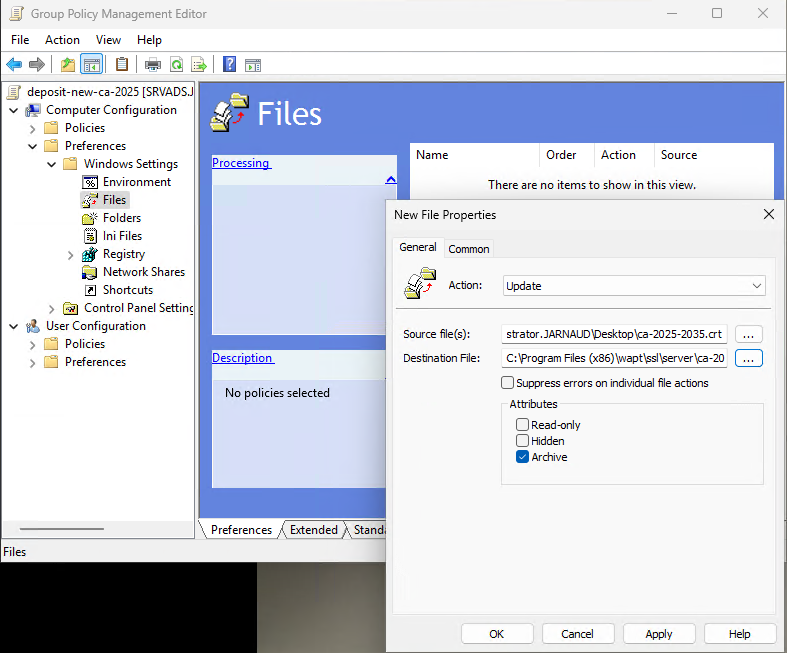
2- Create a GPO that modifies several parameters in the wapt-get.ini file:
Before doing so, consult the existing wapt-get.ini file on your agents.
Make a note of the parameters that need to be changed in order to point your agents to your new server.
Warning
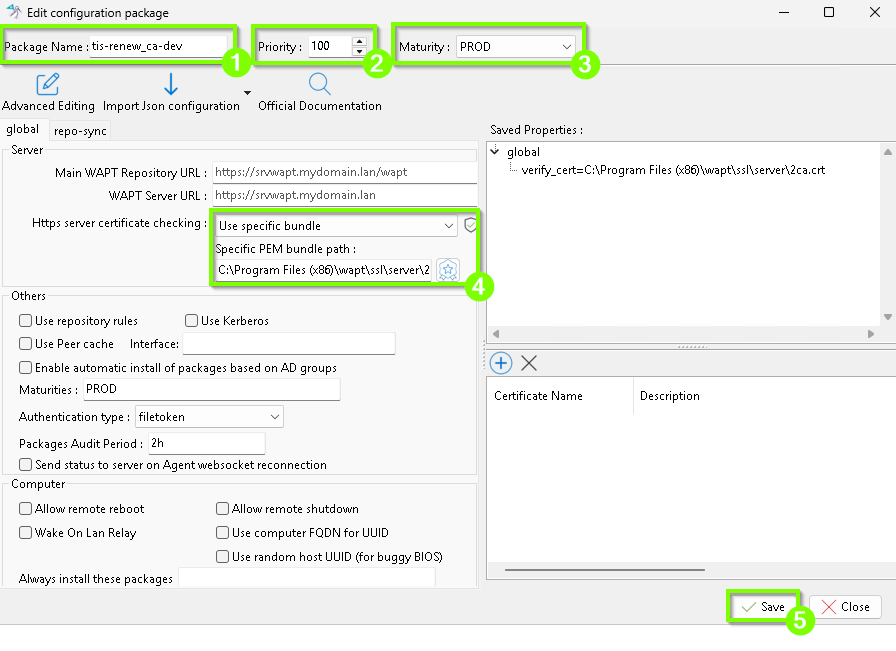
If you were using WAPT configuration packages, you also need to change the [default-global] section.
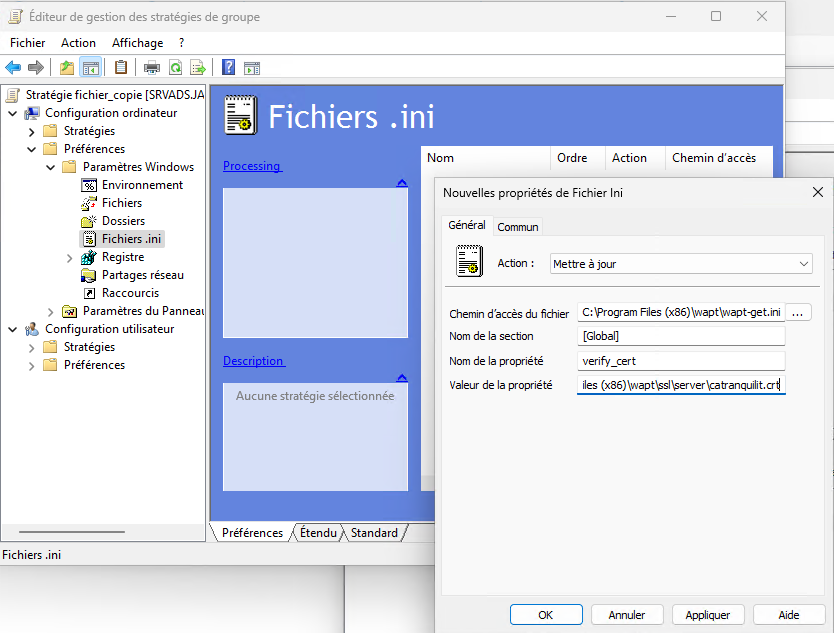
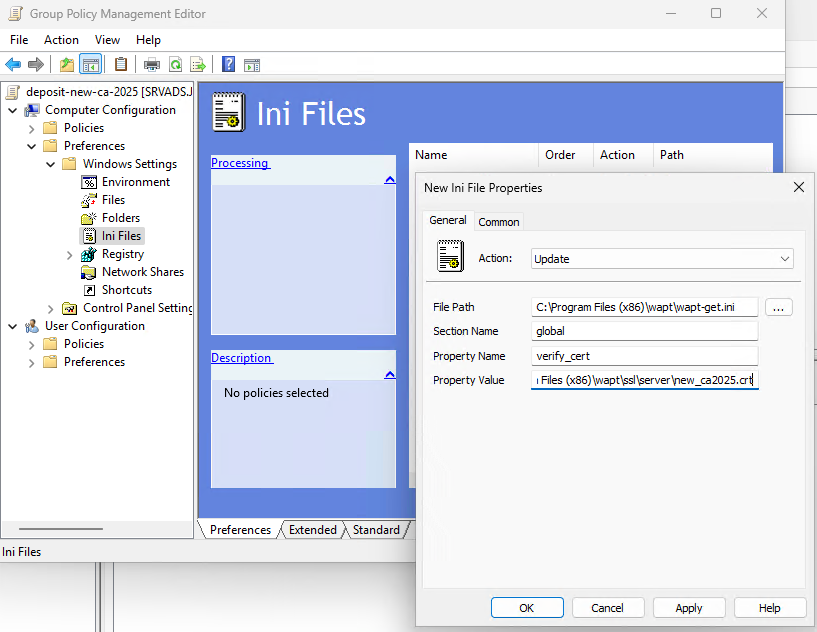
GPO for ini file.¶
In this image, we modify the verify_cert parameter line to pin the new WAPT server certificate.
Other modifications may of course be necessary.
This will allow the agents to switch to the new server and re-establish control over the machines.
3- Set up regular external backups:
Finally, the best solution is to set up regular backups. This will enable a clone to be restored quickly in the event of failure.
2.3. WAPT Server behind a reverse proxy¶
Attention
The support of reverse proxy (WAF, etc.) doing TLS interceptions or TLS terminaison is no longer supported.
If you have a reverse proxy in front of the WAPT server, it has to be configured as a simple TLS forwarding proxy based on SNI (cf. ngx_stream_core_module on nginx server, for example).
First you need to check if the stream module package (libnginx-mod-stream on Debian / Ubuntu, nginx-mod-stream on RedHat and derivatives) is installed on the NginX Reverse Proxy server.
Then you can insert the following content into
/etc/nginx/modules-enabled/80-stream.confof the NginX Reverse Proxy server:
stream {
tcp_nodelay on;
map $ssl_preread_server_name $https_upstream {
wapt.mydomain.com 192.168.2.5:443; # 192.168.2.5 is the local IP address of the WAPT server
}
server {
listen 443;
resolver 127.0.0.1;
proxy_pass $https_upstream;
ssl_preread on;
}
}
Similar configuration is possible using HAProxy TLS Passthrough module but we do not provide support. Please refer to the corresponding documentation for details.
2.4. Resetting the WAPT Linux Server password¶
It sometimes happens to setup a WAPT Server and then forget its password.
To reset the WAPT Console SuperAdmin password you have to relaunch the post-configuration process on the WAPT Server:
Connect to the WAPT Server with SSH.
Connect with user root (or use sudo).
Launch the post-configuration script.
2.5. Problems when enabling enable-check-certificate¶
2.5.1. Message “Certificate CN ### sent by the WAPT Server does not match URL host ###”¶
This means that the CN in the certificate sent by the WAPT Server does not match the value of the wapt_server attribute in the wapt-get.ini file of the WAPT Agent.
There are 2 solutions:
Check the value of
wapt_serverin thewapt-get.inifile of the WAPT Agent.
If the value is correct, this surely means that an error has happened during the generation of the self-signed certificate during the WAPT Server post-configuration (typing error, …).
You MUST then regenerate your self-signed certificates.
On the WAPT Server, delete the content of the
/opt/wapt/waptserver/apache/ssl/folder.
Then, relaunch the post-configuration script (the same as the one used during initial installation, with the same arguments and values).
Then, be sure that the value of FQDN for the WAPT Server is correct.
You may now retry enable-check-certificate.
2.6. What can go wrong during the upgrades of WAPTserver ?¶
The most common issue with the upgrading process is the local antivirus blocking the installation (WAPT is a software installer that keeps a websocket opened to a central management server, so this behavior may be flagged as suspicious by an antivirus, even though this method is the basis of end point management…). If you have an issue when deploying the upgrade, please check your antivirus console and whitelist the waptagent.exe. Another option is to re-sign the waptagent.exe binary if your organization has an internal code signing certificate.
The second most common issue is that for some reason another program is locking a DLL that ships with WAPT. This can happen with poorly designed software installers that pick up the local
%PATH%variable first and then find WAPTs own openssl or python DLL.The third most common issue is a defective Windows install, that does not run scheduled tasks properly, and yes we have seen this!